
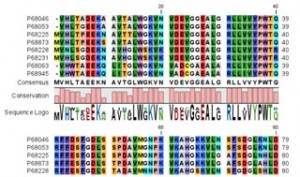
To analyze phytoplankton communities without cross-reactivity with predominant bacteria, a new phytoplankton-specific 23S universal primer set was designed by modifying two previously used ones. Microbial community structures of harmful algal bloom (HAB) caused by Heterosigma akashiwo in Geoje were analyzed using the MiSeq platform. Genomic analysis of red-tide water bloomed with Heterosigma akashiwo in Geoje. Cite this article Kang H, Yoon T, Yoon S, Kim HJ, Park H, Kang C, Kim H. For attribution, the original author(s), title, publication source (PeerJ) and either DOI or URL of the article must be cited. Licence This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, reproduction and adaptation in any medium and for any purpose provided that it is properly attributed.
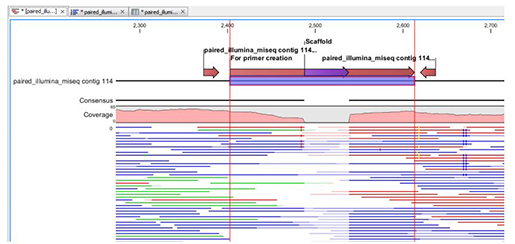
Copying the samples with sufficient coverage will give you a new list of sequences that you can use in your following analyses.5 School of Environmental Science and Engineering, Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology, Gwangju, Republic of Korea DOI 10.7717/peerj.4854 Published Accepted Received Academic Editor Joseph Craine Subject Areas Ecology, Genomics, Marine Biology, Molecular Biology Keywords Red-tide, HABs, Algal bloom, PCR, Coastal water, Next generation sequencing, Microorganism Copyright © 2018 Kang et al. In the next wizard window you can decide to Copy samples with sufficient coverage as well as to Copy the discarded samples. 2: Output table from the Filter Samples Based on Number of Reads tool. The primary output is a table describing how many reads are in a particular sample and if they passed or failed the quality control (see figure 5.2).įigure 5. The algorithm filters out all samples whose number of reads is less than the minimum number of reads or less than the minimum percent from the median times the median number of reads across all samples. The threshold for determining whether a sample has sufficient coverage is specified by the parameters minimum number of reads and minimum percent from the median. This check ensures that the samples are comparable, as the number of reads before merging paired reads is twice as great as the number of merged reads. The tool requires that the input reads from each sample must be either all paired or all single. Toolbox | Microbial Genomics Module ( ) | Metagenomics ( ) | Amplicon-Based Analysis ( ) | Filter Samples Based on Number of Reads ( ) These samples should be excluded from further analysis using the Filter Samples Based on Number of Reads tool. Sometimes, however, DNA extraction, PCR amplification, library construction or sequencing has not been entirely successful, and a fraction of the resulting sequencing data will be represented by too few reads. In order to cluster accurately samples, they should have comparable coverage.
Clc genomics workbench number of reads too low license#

Licensing Server Extensions on a CLC Server.Download a static license on a non-networked computer.Download a license using a license order ID.Licensing requirements for the CLC Microbial Genomics Module.Legacy MLST schemes visualization and management.Download Custom Microbial Reference Database.Download Curated Microbial Reference Database.Download Amplicon-Based Reference Database.Estimate Alpha and Beta Diversities workflow.Merge and Estimate Alpha and Beta diversities.Analyze Viral Hybrid Capture Panel Data.MLST Scheme Visualization and Management.Getting started with the MLST Scheme tools.Visualization of K-mer Tree for identification of common reference.Visualization of SNP Tree including metadata and analysis result metadata.Phylogenetic trees using SNPs or k-mers.The Find Best References using Read Mapping Report.Find Best References using Read Mapping.From samples best matches to a common reference for all.Filtering in a SNP-Tree creation scenario.Running an analysis directly from a Result Metadata Table.Associating data elements with metadata.Handling of metadata and analysis results.Introduction to Typing and Epidemiology.Importing and exporting OTU abundance tables.Create taxonomic level subtables for heat maps.Filter Samples Based on Number of Reads.The concept of CLC Microbial Genomics Module.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
